Project Based Learning Curriculum and Assessment
Project Based Learning (PBL) curriculum and assessment drives deeper learning and builds real-world success skills.

Project Based Learning Curriculum and Assessment
Project Based Learning (PBL) curriculum and assessment drives deeper learning and builds real-world success skills.
What is Project Based Learning (PBL) Curriculum?
Discover PBL curriculum designed for educators and schools seeking engaging, real-world learning experiences. Our curriculum includes ready-to-use projects, teaching guides, and embedded assessment tools, helping teachers implement high-quality Project Based Learning (PBL) with confidence and efficiency. With PBLWorks’ approach, schools can support deeper learning and meaningful student outcomes from day one.
In today's dynamic educational landscape, PBL stands out as a leading model for improving student engagement and outcome, particularly among students who are furthest from opportunity or with limited access to educational equity. Results from a study on the effect of PBL on student engagement and educational outcomes offer compelling evidence:
"In a randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 3,645 students in five large urban districts engaged in both AP Environmental Science and AP U.S. Government and Politics PBL courses and traditional courses, researchers from the University of Southern California (USC) found that students in AP PBL courses outperformed students in traditional AP courses by 8 percentage points. Results for students from low-socioeconomic backgrounds were comparable to their peers from higher socioeconomic backgrounds."
But exactly what is Project Based Learning (PBL)?
In short, PBL is an educational methodology built around interactive, real-world problem solving over and extended period of time.
Differing from traditional learning models, project-based education encourages student-centered learning, focusing on both the retention of knowledge and the development of skills that can be applied within and beyond the classroom. PBL's effectiveness stems from the authenticity and relevance of PBL curriculum, which emphasizes in-depth exploration of complex driving questions and practice with competencies such as critical thinking, collaboration, creativity, and communication.
With the potential to transform student experiences, Project Based Learning curriculum is vital to the success of the modern education system. Why PBL? Simply put, PBL offers some key benefits that traditional models often struggle to deliver: model:
- Better engagement with course material
- Deeper understanding of key concepts
- Greater awareness of future career opportunities
- More meaningful impact on real problems
- Stronger skills for success in work and life
- More invested, fulfilled teachers
- Further exposure to technology tools and creative processes
Without doubt, PBL is effective and important for student engagement and improved learning, but effective implementation requires an intentional investment of time and resources. If you want to learn how to make the most of PBL curriculum for your school, the rest of this page will be your guide.
The PBL Approach: Methodology and Framework
The key to high-quality Project Based Learning lies in a few elements that are central to the PBL approach: a challenging question to answer or explore; student-centered learning focused on knowledge and skills development; and an opportunity for students to present their work in a public setting for real-world evaluation and implementation. By combining classroom instruction with immersive problem-solving opportunities, the Project Based Learning methodology gives students a richer, more engaging educational experience.
The Role of the PBL Driving Question
PBL education revolves around the driving question—a complex, compelling inquiry into a publicly relevant topic, ideally one that lacks general consensus about the best way to answer or address it. The cornerstone of all PBL curricula, driving questions can be particularly useful for teaching controversial topics that tend to polarize students with differing viewpoints. In all cases, by prioritizing driving questions to facilitate a Project Based Learning framework, teachers can create a safe space for inclusive dialogue that rewards open-mindedness, adaptability, and intellectual growth, empowering students to think critically about all aspects of a problem before forming solutions.
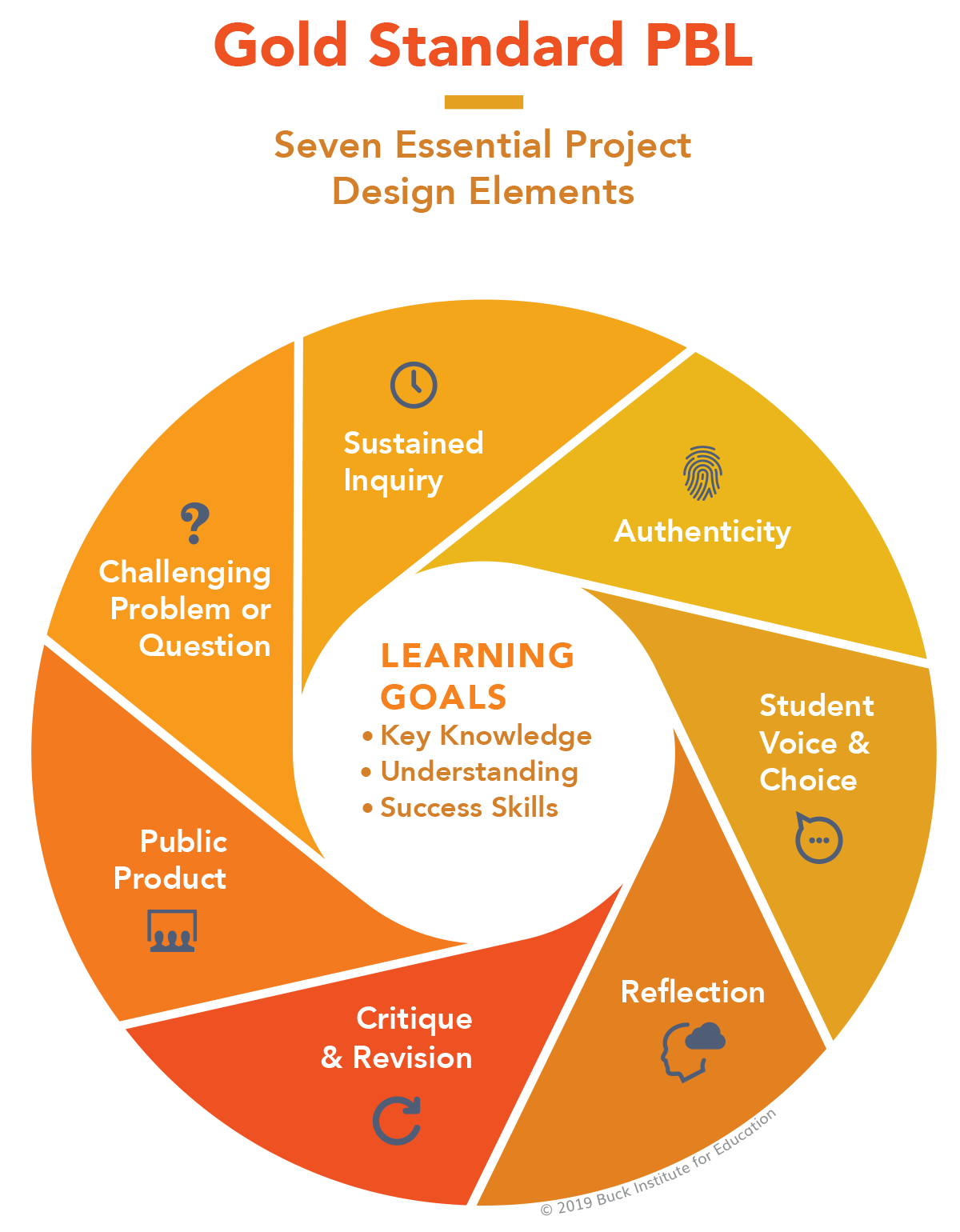
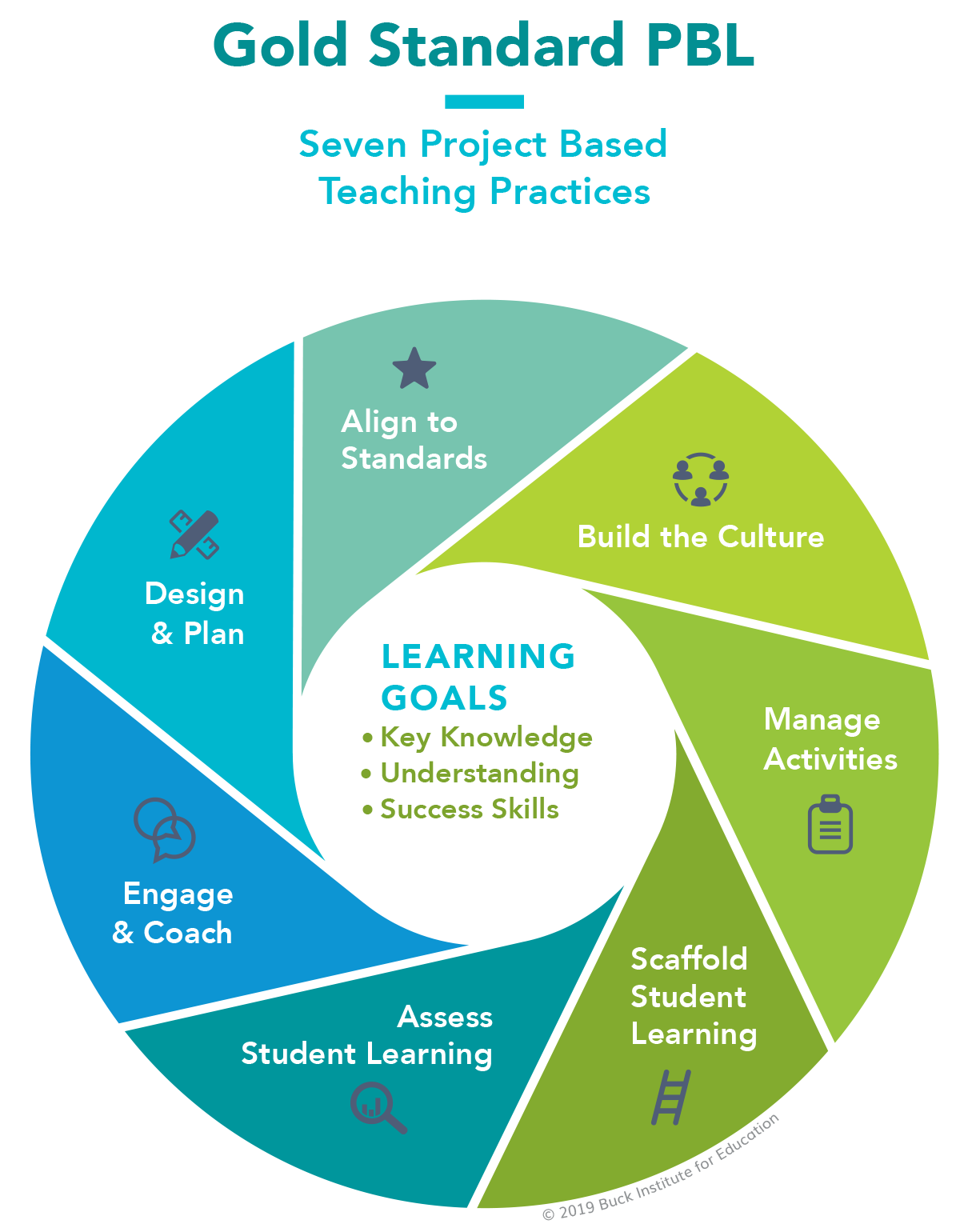
Gold Standard PBL
At PBLWorks, we apply high-quality Project Based Learning methodologies in our Gold Standard PBL model. Comprehensive and informed by extensive research, Gold Standard PBL guides teachers and schools on best practices for project design and teaching methods to ensure effective PBL implementation and support student learning.
Gold Standard Project Design employs seven essential elements:
- Driving question
- Student voice and choice
- Sustained inquiry
- Authenticity
- Reflection
- Critique and revision
- Public product
Similarly, Gold Standard Teaching Practices use seven project-based methods to deliver successful outcomes for students—inside and outside the classroom:
- Design and plan
- Align to standards
- Build the culture
- Manage activities
- Scaffold student learning
- Assess student learning
- Engage and coach
Why go to the trouble of designing PBL curriculum? Because when it comes to educational opportunity and degree of student development, Project Based Learning is the gold standard.
Benefits and Advantages of Project Based Learning
Of the many Project Based Learning benefits, student engagement is the most critical. Engaged students—those who take an active role in their own learning and who form a genuine interest in exploring concepts and course material—are more likely to graduate on time than students who are not fully engaged in the learning process. With its emphasis on relevant, real-world applications and deep inquiry into meaningful topics, a well-executed PBL curriculum offers a superior mechanism for capturing (and keeping) student attention, promoting autonomy and agency, and fostering long-lasting learning.
In addition to providing deeper understanding of core concepts, PBL supports student success skill development by delivering regular opportunities for applied practice of critical thinking, collaboration with peers and community experts, creative execution, and effective communication. The process of translating academic knowledge into applications that produce real effects creates a powerful connection between learning and acting, improving student motivation and creating confidence to aid future career pursuits.
Of course, student success depends partly on the availability and retention of qualified teachers—a growing concern amid a national teacher shortage. To be at their best, teachers need support for their own continued learning and chances to collaborate with colleagues in an engaging environment. Among other PBL advantages, high-quality professional learning opportunities for teachers who want to offer Project Based Learning curricula can improve job satisfaction and support greater teacher retention over time.
While the evidence shows how effective PBL education can be when done well, Project Based Learning requires a plan for how to implement it—starting with designing an effective project-based learning curriculum.
Designing a Project Based Curriculum
Creating any curriculum from scratch can feel intimidating, especially if you’re adopting a new teaching model such as Project Based Learning for the first time. But when it comes to PBL curriculum, the promise of better student outcomes is worth the upfront effort. With a little guidance, you can design a project-based curriculum for K-12 educators—and you can make the case for Project Based Learning curriculum in your classroom.
Aligning PBL with Academic Standards
A common concern among those considering PBL is how to ensure the curriculum aligns with required academic standards such as Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) for science, Common Core for math and English language arts (ELA), and the College, Career, and Civic Life (C3) Framework for social studies. For PBL, projects need to reinforce required knowledge and skills to give teachers confidence that they can replace traditional learning models without sacrificing academic relevance or critical content. To do that, a good Project Based Learning curriculum will incorporate specific elements.
PBL Curriculum Key Components and Structure
High-quality PBL instruction relies on some key components and a consistent structure to deliver deep, relevant learning. PBLWorks offers pre-packaged lesson plans and PBL curriculum ideas that incorporate those key components organized under the Gold Standard PBL model:
- Overview of each project’s driving question, entry event, major products, and target audience
- List of relevant content standards and success skills addressed by each project
- Rubrics for assessing student learning, evidenced by major products and smaller deliverables
- Daily step-by-step lessons for the duration of each project
- Supplemental resources such as handouts, readings, and video content
Using the necessary components and recommended project structure, teachers can seamlessly transition from traditional instruction methods to Project Based Learning—all while adhering to academic standards and providing a more equitable, effective learning experience for all students.
Examples of Project Based Learning Curriculum in Action
What does PBL curriculum look like in action? A hallmark of Project Based Learning is its versatility, so effective Project Based Learning examples can manifest in many different ways. A sign that PBL is working well is a classroom full of highly engaged students representing different backgrounds, experiences, and learning styles. You might also see marked improvement in success skills such as critical thinking and communication over the course of a school year. And ideally, teachers report greater satisfaction and support in their educator roles.
Project-Based Curriculum Examples
Still not sure what goes into a PBL curriculum unit? Here are a few PBL project examples that demonstrate Gold Standard PBL in action:
Teachers on PBLWorks TEACH
Curious about how to implement PBL at your school? Hear from a fellow educator about their experience using pre-designed Project Based Learning curriculum modules from PBLWorks TEACH:
Assessment in PBL: Measuring What Matters
After implementing Project Based Learning, you need a way to gauge the model's effectiveness. Does PBL create better educational outcomes or not? Are students learning the content you intended? To answer these and similar questions, tools for PBL assessments are imperative.
In PBL, assessment differs from traditional grading. Traditional grading assigns a numerical value to measure knowledge of specific concepts. Project Based Learning goes further by also evaluating practical learning through performance-based assessments. Because PBL is competency-based education focused on real-world learning, measurement of student development employs authentic assessment, encompassing both knowledge and skills applied to real-world scenarios. Ideally, assessment is integral to the curriculum itself—also known as curriculum-embedded performance assessment.
PBL Assessment Tools
Assessment comes in two main modes: formative and summative. Formative assessment provides regular, ongoing evaluation of learning over time, giving students opportunities to apply feedback between assessment periods in order to demonstrate improvement. Summative assessment is akin to a final evaluation, offering a cumulative estimation of overall performance relative to a specific goal.
There are a few common tools that help make assessment easier and more consistent:
- PBL rubrics
- Checklists
- Models
- Learning scales
- Peer assessment
- Self-assessment
PBL Assessment Examples
For more detailed guidance, check out a few examples of PBLWorks TEACH assessments:
With an understanding of Project Based Learning curriculum and how to assess its effectiveness, you're ready to bring the benefits of PBL to your school.
Getting Started with PBL Curriculum
So you want to implement PBL at your school? That's great! It's a proven curriculum model capable of transforming student learning and educational outcomes. Get started in a few steps:
- Establish your vision for how PBL will benefit students and the greater school community.
- Select or design projects that hold relevance for your student population and align with academic standards for specific subjects.
- Curate supplemental resources and plan learning experiences that will challenge students to explore new ideas and deepen their understanding of core concepts.
- Perform regular assessments to evaluate both knowledge and skills development over time.
- Update your curriculum and teaching practices periodically to adapt to an evolving social and educational environment.
If you want hands-on help getting started or need additional Project Based Learning curriculum ideas, PBLWorks offers a comprehensive three-day PBL 101 workshop.
For ongoing professional development to take your PBL expertise to the next level, check out a few additional resources:
Implementing PBL is an iterative process. It takes time and intention to hone, but the results of a well-executed Project Based Learning curriculum are rewarding and well worth the effort—for students and teachers alike.

PBLWorks TEACH: a Complete PBL Curriculum and Assessment Solution
By now, it should be clear that high-quality PBL focused on student-centered learning holds an advantage over traditional instruction models. Relevant, real-world experimentation and application of core concepts fosters sustained engagement, builds student autonomy and agency, and promotes deeper learning. Engaged students demonstrate more success in the classroom and learn practical skills that set them up to succeed beyond school as well.
Teachers who believe in Project Based Learning and need help implementing the model or advancing their own PBL teaching skills now have access to ready-to-use curriculum units developed by PBLWorks, the leading experts in Project Based Learning. The high-quality instructional materials (HQIM) available online through PBLWorks TEACH offer standards-aligned lessons for math, science, ELA, and social studies.
With TEACH, educators and school administrators can more easily and effectively put PBL into practice, with pre-designed curriculum and integrated professional training, all supported by PBLWorks's extensive domain experience and expertise.
Features of PBLWorks TEACH include:
- Units based on Gold Standard PBL project design principles and teaching practices
- Structured, scalable approach for efficient implementation and management
- Embedded professional learning
- Integrated performance assessments
- Step-by-step instructions for teachers delivering PBL lessons
- Easy-to-use online platform with ready-made materials
Ready to put PBL into practice at your school? Start today with PBLWorks TEACH.